
The main focus of Kali Linux 2023.3 is overhauling the project's internal infrastructure stacks. The goals are to simplify and standardize key components like Debian 12, Cloudflare for CDN/WAF, Nginx web server, and Ansible for infrastructure as code.
Kali is also automating more processes such as testing package builds and migrating packages between versions with the release of Kali Autopilot, which was first released with Kali Purple in Kali 2023.1.
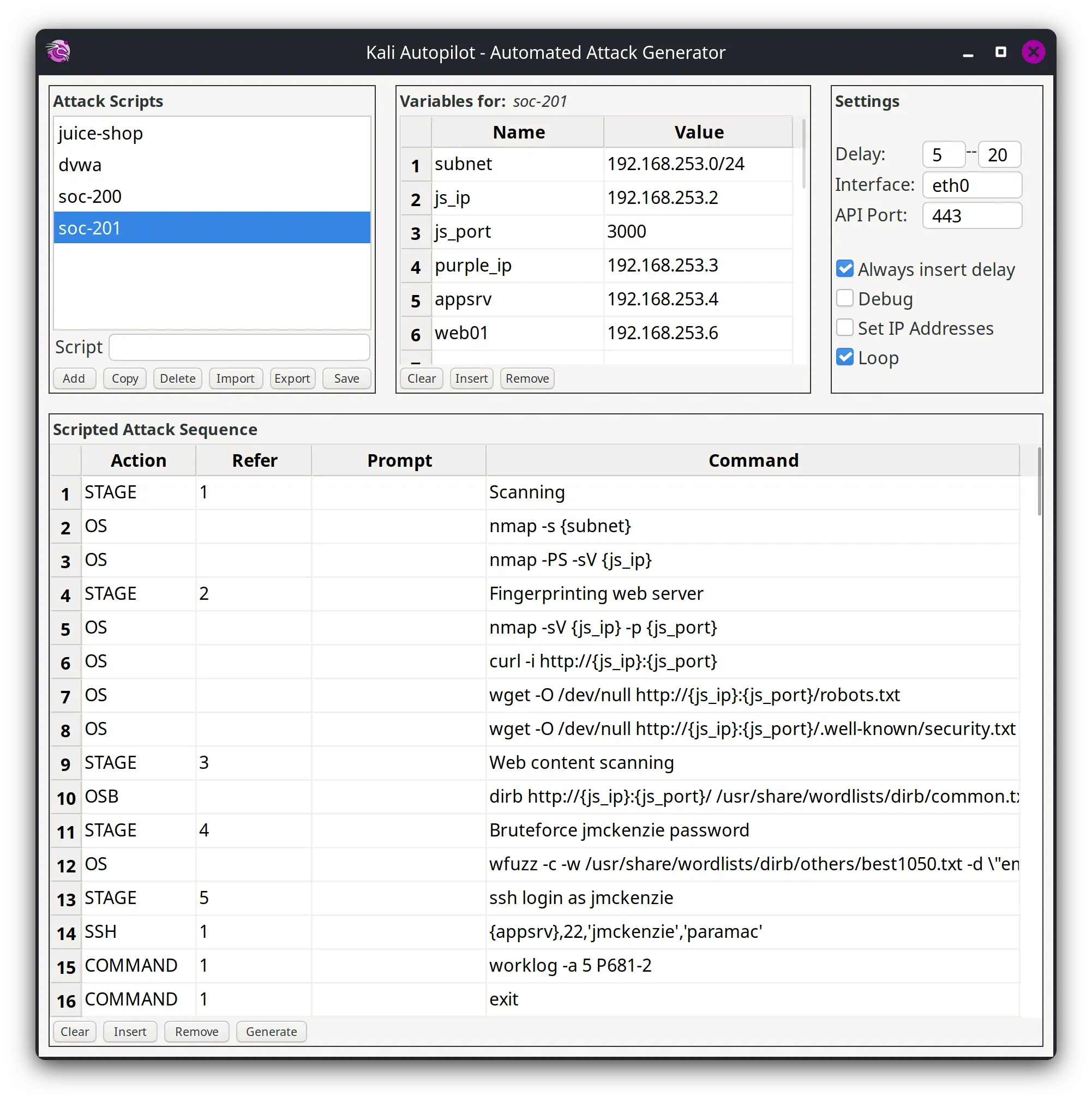
What is Kali Autopilot?
Kali Autopilot is an automated attack framework. It is a bit like an “AutoPwner”, which follows pre-defined “attack scenarios”.
Another major change is the launch of mirror-traces.kali.org to provide more detailed troubleshooting information for Kali's community mirror administrators. The git repository for this status tracking tool is available publicly as part of Kali's efforts to work more openly.
Kali Autopilot framework runs predefined attack scenarios to test defenses like intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and SIEM solutions.
9 New Tools Introduced in Kali
Kali Linux 2023.3 brings 9 new information security tools:
- Calico - Cloud native networking and network security
- cri-tools - CLI and validation tools for Kubelet Container Runtime Interface
- Hubble - Network, Service & Security Observability for Kubernetes using eBPF
- ImHex - A Hex Editor for reverse engineers, programmers and people who value their retinas when working at 3 AM
- kustomize - Customization of kubernetes YAML configurations
- Rekono - Automation platform that combines different hacking tools to complete pentesting processes
- rz-ghidra - Deep ghidra decompiler and sleigh disassembler integration for rizin
- unblob - Extract files from any kind of container formats
- Villain - C2 framework that can handle multiple reverse shells, enhance their functionality and share them among instances
Along with new tools being added to Kali, there has been numerous packages have been updated including Greenbone, Humble, Impacket, jSQL, OWASP ZAP, Rizin, Tetragon, theHarvester, and Wireshark.
For mobile penetration testing, Kali NetHunter has a new app and terminal interface. Device support has been added for the Nothing Phone (1) and Samsung Galaxy A7. Raspberry Pi Zero W now boots to the command line by default like the Pi 1 image.
How to Install Kali Linux 2023.3
To start using Kali Linux 2023.3, users can upgrade their existing installation with the below steps or directly download ISO images for new installs and live distributions.
If you already have an existing Kali Linux installation then you can easily upgrade to the Kali latest version with the following command-
┌──(r00t㉿cyberkendra)-[~] └─$ echo"deb http://http.kali.org/kali kali-rolling main contrib non-free non-free-firmware" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list ┌──(r00t㉿cyberkendra)-[~] └─$ sudo apt update && sudo apt -y full-upgrade ┌──(r00t㉿cyberkendra)-[~] └─$ cp -vrbi /etc/skel/. ~/ ┌──(r00t㉿cyberkendra)-[~] └─$ [ -f /var/run/reboot-required ] && sudo reboot -f
Once the upgrading process is completed, you can check if the upgrade was successful by using the following command:
┌──(r00t㉿cyberkendra)-[~] └─$ grep VERSION /etc/os-release
The major infrastructure changes in Kali Linux 2023.3 are still a work in progress. More upgrades are planned for future releases as the project continues its emphasis on automated security testing. Kali Linux remains focused on empowering defenders to proactively find weaknesses before attackers can exploit them.