
The software giant reports observing an uptick in campaigns that abuse services like SharePoint, OneDrive, and Dropbox to deliver malicious content and compromise user identities.
Microsoft said, these sophisticated attacks, which have been on the rise since mid-April 2024 that involve files with restricted access and view-only restrictions, and also employ advanced defense evasion tactics that make them particularly challenging to detect and mitigate.
The primary goal of these campaigns appears to be identity compromise, often leading to business email compromise (BEC) attacks, financial fraud, data exfiltration, and lateral movement within target networks.
"The files sent through the phishing emails are configured to be accessible solely to the designated recipient," it said. "This requires the recipient to be signed in to the file-sharing service — be it Dropbox, OneDrive, or SharePoint — or to re-authenticate by entering their email address along with a one-time password (OTP) received through a notification service."
Key Features of the Attack:
- Exploitation of Trust: Threat actors compromise accounts within trusted vendor organizations, using their legitimate file hosting services to share malicious files with targets. This approach exploits the inherent trust between business partners, increasing the likelihood of successful phishing attempts.
- Sophisticated Evasion Techniques: Attackers are increasingly employing two main tactics to evade detection:
- Files with restricted access: Shared files are configured to be accessible only to the intended recipient, requiring authentication to view.
- View-only restrictions: Files are set to "view-only" mode, preventing downloads and hampering analysis by email detonation systems.
- Social Engineering: File names are crafted to appear legitimate, often referencing ongoing business processes, urgent matters, or IT-related topics to entice users to interact with the shared content.
- Multi-Stage Attack Chain: The typical attack flow involves:
- Initial compromise of a trusted vendor account
- Hosting of a malicious file on a legitimate service
- Sharing the file with the target organization
- Exploiting automated sharing notifications from trusted services
- Redirecting victims to adversary-in-the-middle (AiTM) phishing pages
- Identity Compromise: The final stage involves capturing user credentials and multi-factor authentication (MFA) tokens, potentially leading to account takeover and further malicious activities.
Microsoft's advisory emphasizes the evolving nature of these threats, noting that the abuse of file hosting services for phishing has been trending over the past few years. The company stresses that while these campaigns are often opportunistic, they demonstrate a high level of sophistication in their execution.
To combat these threats, Microsoft recommends several mitigation strategies:
- Implementing Conditional Access policies in Microsoft Entra, with a focus on risk-based access controls
- Enabling continuous access evaluation
- Adopting passwordless authentication methods, such as FIDO2 security keys
- Deploying network protection features in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- Implementing mobile threat defense solutions
- Utilizing advanced browser security features and email protection systems
"While these campaigns are generic and opportunistic in nature, they involve sophisticated techniques to perform social engineering, evade detection, and expand threat actor reach to other accounts and tenants," the Microsoft Threat Intelligence team said.
Another development comes from Sekoia, detailing a new AitM phishing kit called Mamba 2FA that's sold as phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) to other threat actors to conduct email phishing campaigns that propagate HTML attachments impersonating Microsoft 365 login pages.
Mamba 2FA was first documented by Any.Run analysts in late June 2024, but Sekoia reports that it has been tracking activity linked to the phishing platform since May 2024.
Additional evidence shows that Mamba 2FA has been supporting phishing campaigns since November 2023, with the kit being sold on ICQ and later on Telegram, on a subscription basis for $250 per month. It supports for Microsoft Entra ID, AD FS, third-party SSO providers, and consumer accounts.
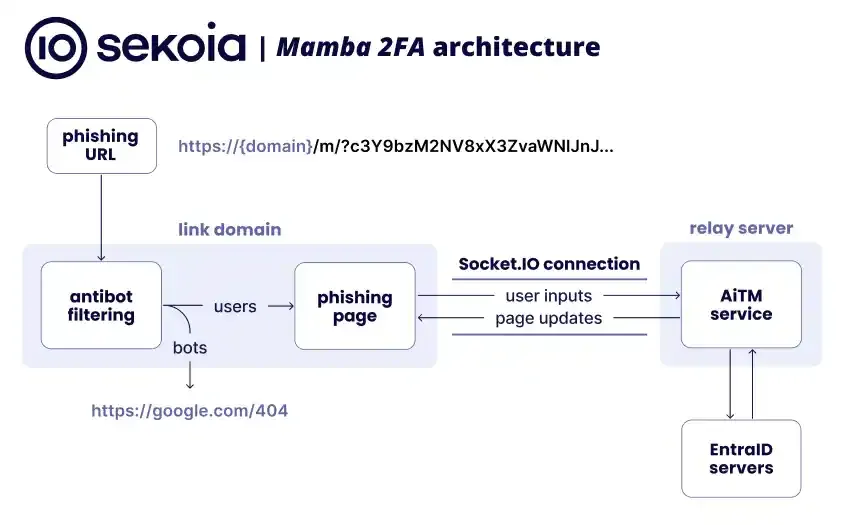 |
| Architecture of the Mamba 2FA phishing kit. |
Mamba 2FA offers phishing templates for various Microsoft 365 services, including OneDrive, SharePoint Online, generic Microsoft sign-in pages, and fake voicemail notifications that redirect to a Microsoft login page.
For enterprise accounts, the phishing pages dynamically assume the targeted organization's custom login branding, including logos and background images, making the attempt appear more authentic.
Both the advisory includes detailed information on relevant Microsoft Defender XDR detections and provides hunting queries to help security teams identify potential compromises related to these attack techniques.